Microfrontends
In a traditional microservice architecture, the application consists of a number of fine-grained loosely coupled microservices, each of those exposing its API. However, the UI which interfaces with a user is still a monolithic application, which means that the frontend is neither fine-grained or loosely coupled and suffers from similar issues than a monolith backend service.
Source: https://micro-frontends.org/
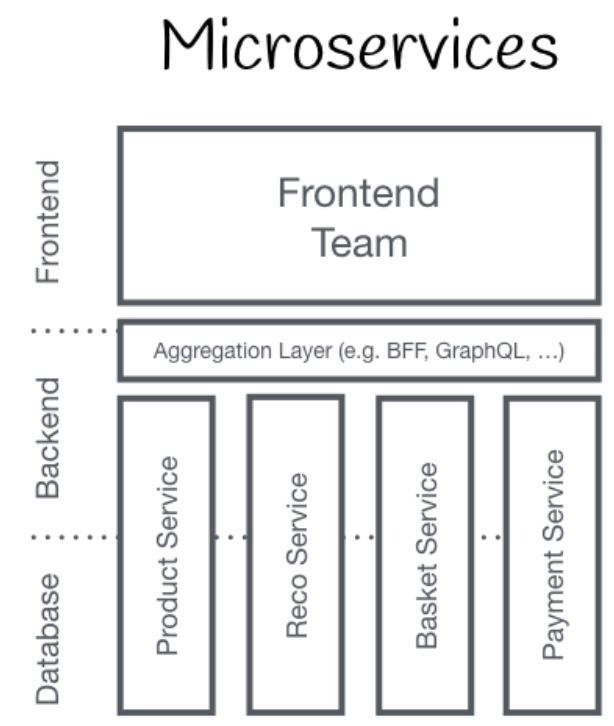
Microfrontends bring the idea of microservices further into the area of User Interfaces. Now, each service can provide a part of a frontend-application, called Microfrontend. All microfrontends are - at runtime - loaded and executed together in a single web application.
Source: https://micro-frontends.org/
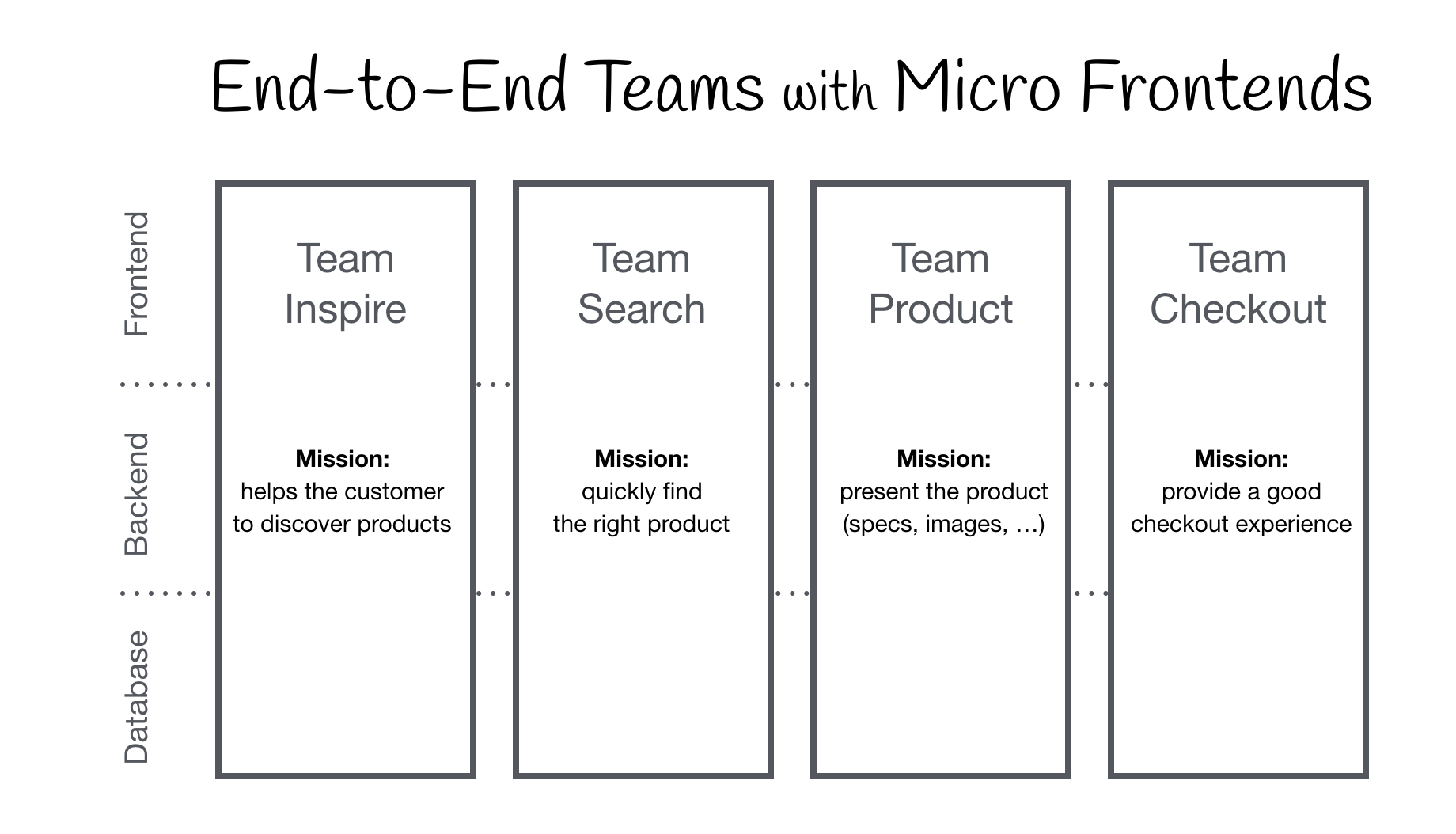
A typical Mosaic (micro) service consists of a backend and a (micro)frontend.
Management System as a Shell
The Mosaic user interface, also known as Management System (or sometimes Content Management System / CMS), is built using microfrontends. It functions as a centralized shell that hosts multiple microfrontends at runtime. This shell combines platform-level microfrontends (such as Home and Navigation) with microfrontends from managed and customizable services.
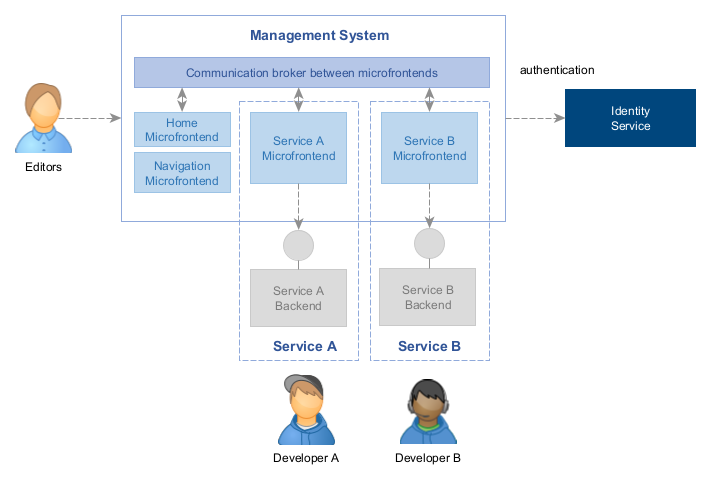
This architecture allows the separation of the user experience by service, while still providing a consistent Single-Page-Application experience for the user.
Mosaic provides optimized UI components and libraries to seamlessly integrate new microfrontends into the Management System while keeping the user experience consistent and predictable.
Architectural Benefits
By distributing UI responsibility across services that align with backend microservice boundaries, this approach maintains consistency between service architecture and user interface design. Each service owns both its backend logic and its corresponding frontend, supporting independent development and deployment cycles for both.
Extensions
Microfrontends can share Extensions and functionality with other microfrontends. Extensions render individual parts of the UI. Other microfrontends can integrate such exposed extensions. For example, the Image Service exposes an extension which renders a preview of an image and another which allows to browse and select images.
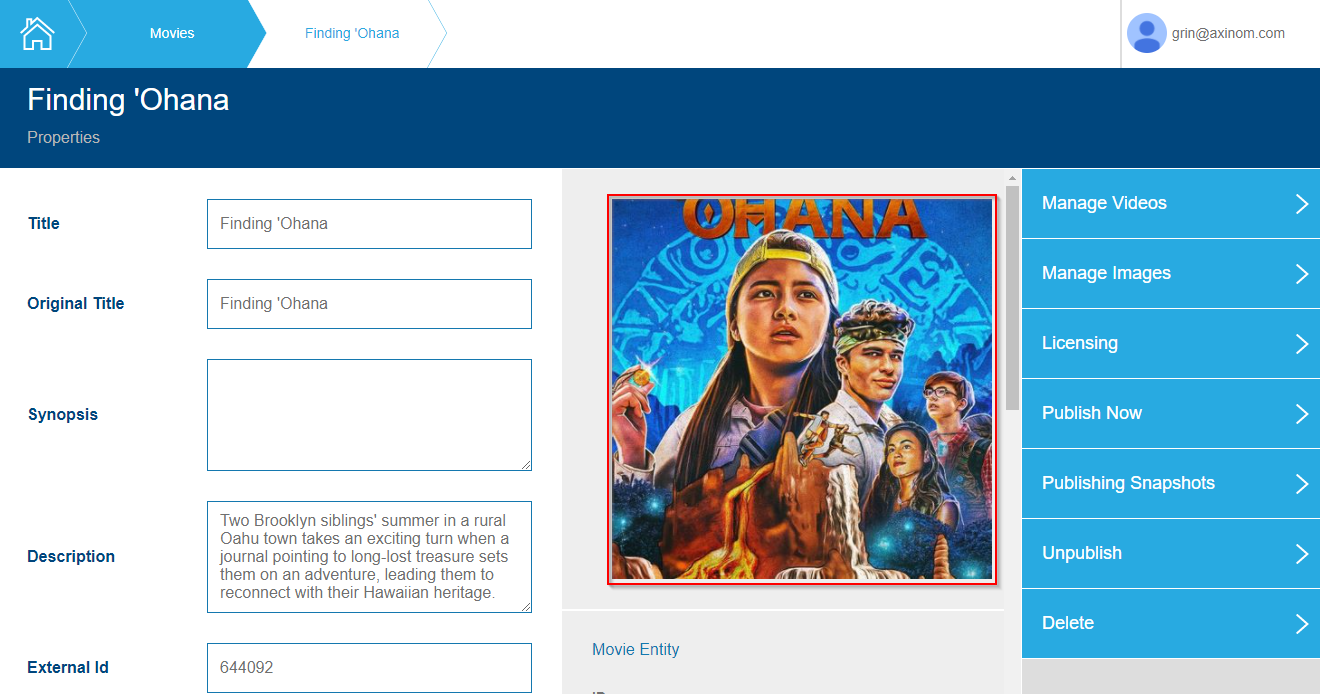 Movie Detail station from the Media Service embedding a cover image, which is an extension exposed by the Image Service
Movie Detail station from the Media Service embedding a cover image, which is an extension exposed by the Image Service
Other microfrontends can integrate an image preview or image selection without knowing any details about their UI.
For more information about the methods and concepts the Mosaic Platform offers to microfrontends to interact with each other and more, have a look at the documentation of the @axinom/mosaic-portal package.